Miniature Fiber Optic Pressure Sensors Based on Polymer Process
Miniature
Fabry-Perot (FP) pressure sensors have been of great interest because of their
advantages of small sizes, high performance, and immunity to electromagnetic
interference. Most of these sensors are built with silicon/silica materials
that have good mechanical, chemical, and thermal stabilities. However, due to
the large elastic modulus of silica/silicon, developing a high sensitivity
miniature sensor becomes difficult. In addition, fabrication of these sensors
often involves high temperature fusion bonding and harsh acid etching. On the
other hand, to realize high sensitivity, miniature pressure sensors, a polymer
material becomes an attractive choice since its Young’s modulus is
significantly smaller than that of silicon/glass. Moreover, polymer processes
can be performed under ambient pressure and temperature without hazardous
chemicals. However, a significant drawback of a
polymer-based sensor is the high temperature sensitivity, which must be
compensated to obtain accurate pressure measurements.
Miniature temperature Compensated Fabry Perot Pressure Sensor Fabricated with Self-aligned Photolithography Process [1, 2]
-
Since
there are many available processing techniques that can be used for polymer
materials and performed in ambient pressure and temperature, sensor fabrication
can be easy by using these processes. In this work, fiber optic Fabry-Perot
sensor fabricated by using a self-aligned photolithography technique is
presented. Instead of using the conventional mask and mask aligner for the
photolithography process, an optical fiber waveguide is used to couple UV light
for exposing and defining the optical cavity. This low-cost fabrication
technique offers self-aligned property for sensor fabrication. Fiber Bragg
gratings were embedded in the sensors to measure temperature and compensate
temperature effect on the polymer cavities. Figure 1 illustrates the
fabrication process of two types of sensors (i.e.: co-axial and cross-axial
sensors) fabricated with the self-aligned photolithography. The cavities
defined by the self-aligned photolithography were covered with another
UV-curable polymer layer and thin metal layer. This polymer/metal composite
layer was used as a pressure sensitivity layer for pressure measurements. The
cross-axial sensor configuration has surface-mountable capability when a
surface-flow should be avoided in pressure measurements.
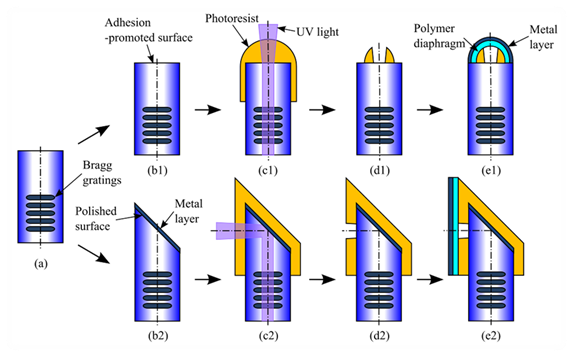
Figure 1: Fabrication process of co-axial and cross-axial sensors
-
Scanning
electron micrographs of the fabricated co-axial and cross-axial sensors are
shown in Figure 2.
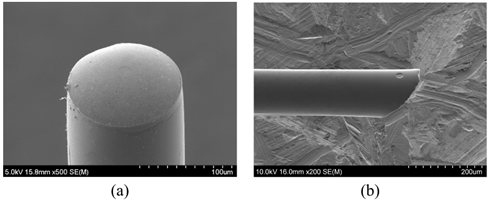
Figure 2: Scanning electron micrographs of fabricated sensors: (a) co-axial sensor and (b) cross-axial sensor.
Miniature Temperature Compensated Fabry-Perot Pressure Sensor Created by Using UV-molding process with an Optical Fiber Based Mold [3]
UV-molding
process (or UV imprinting process) is one of fabrication processes that make
use of a UV curable polymer. The process usually consists of several steps
including master pattern fabrication, mold fabrication, dispensing/exposure,
and demolding. If a master pattern is used as a mold, the first step can be
omitted. This process has been applied to fabricate various optical elements
with small features, which allows for enhanced thermo-mechanical stability, low
birefringence, and low-cost. In this work, a Fabry-Perot (FP) pressure sensor
with built-in temperature measurement and compensation capability is designed
and fabricated based on a UV-molding process and the metal-polymer composite
thin film fabrication method described previously. Figure 3 illustrate the
fabrication process of the sensor.
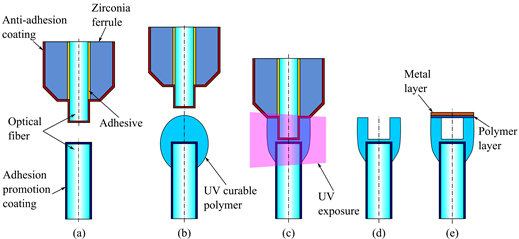
Figure 3: Fabrication process of UV-molded fiber optic pressure sensor.
The
sensor is composed of a UV-molded optical cavity and a polymer-metal composite
diaphragm, which is fabricated at the end of a single mode fiber with a
pre-written fiber Bragg grating, rendering the sensor the capability of
temperature compensation and simultaneous measurement of pressure and
temperature. The mold used for UV-molding process is built by assembling a
polished ferrule and a cleaved optical fiber, which eliminates the need for a
costly semiconductor or direct machining process and enables high accuracy
optical alignment of the mold and the sensing fiber. The sensor fabrication
follows simple, repeatable processes and safe procedures, and uses less
expensive materials and equipment. This fabrication method can also be used for
batch fabrication or wafer scale fabrication with minor modifications to the
processes. Scanning electron micrographs of the fabricated co-axial and
cross-axial sensors are shown in Figure 4.
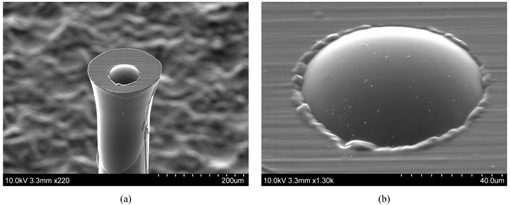
Figure 4: SEM images of (a) fabricated sensor and (b) diaphragm close-up.
Publications on this work
[1] Bae,
H., Zhang, X. M., Liu, H., & Yu, M., ”Miniature
surface-mountable Fabry-Perot pressure sensor constructed with a 45 degree angled
fiber,” Optics
Letters, 35(10), 1701–1703 (2010).
[2]
Bae, H., Dunlap, L., Wong, J., & Yu, M., “Miniature Temperature Compensated
Fabry – Perot Pressure Sensors Created With Self-Aligned Polymer
Photolithography Process,” IEEE Sensors Journal, 12(5) (2012).
[3]
Bae, H., & Yu, M., “Miniature Fabry-Perot pressure sensor created by using
UV-molding process with an optical fiber based mold,” Optics Express, 20(13),
(2012).
Copyright by Sensors and Actuator Lab
Last updated on September 10th, 2010